A storm has knocked out power to your beach house, and you would like to build a battery from household items to charge your iPhone. You have the following materials. alum in the kitchen, which can be used to make a 1.0 M Al3+ solution bleach, which is a solution that is approximately a 1.0 M in ClO-aluminum foil, a platinum necklace and bologna, which can be used as a salt bridge (a) What are the half-reactions and overall reaction in the battery?

For a lead storage battery: (a) Sketch one cell that shows the anode, cathode, electrolyte, direction of electron and ion flow, and sign of the electrodes. (b) Write the anode, cathode, and overall cell reactions. (c) Calculate the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction (E° = 1.924 V). (d) What is the cell voltage when the cell reaction reaches equilibrium?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Electrochemical Cells
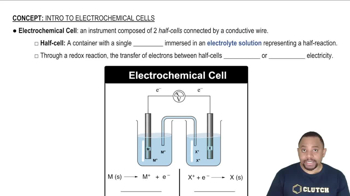
Cell Reactions and Standard Electrode Potentials

Equilibrium Constant and Cell Voltage

A storm has knocked out power to your beach house, and you would like to build a battery from household items to charge your iPhone. You have the following materials. alum in the kitchen, which can be used to make a 1.0 M Al3+ solution bleach, which is a solution that is approximately a 1.0 M in ClO-aluminum foil, a platinum necklace and bologna, which can be used as a salt bridge (b) What voltage can be generated?
A storm has knocked out power to your beach house, and you would like to build a battery from household items to charge your iPhone. You have the following materials. alum in the kitchen, which can be used to make a 1.0 M Al3+ solution bleach, which is a solution that is approximately a 1.0 M in ClO-aluminum foil, a platinum necklace and bologna, which can be used as a salt bridge (d) An iPhone requires 5.0 V for charging. Can this battery charge the phone? Explain.
A mercury battery uses the following electrode half-reactions: (b) Calculate ∆G° (in kilojoules) and K at 25 °C for the cell reaction.
A mercury battery uses the following electrode half-reactions: (c) What is the effect on the cell voltage of a tenfold change in the concentration of KOH in the electrolyte? Explain..
