Textbook Question
A mercury battery uses the following electrode half-reactions: (b) Calculate ∆G° (in kilojoules) and K at 25 °C for the cell reaction.

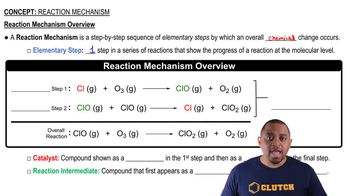
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


A mercury battery uses the following electrode half-reactions: (b) Calculate ∆G° (in kilojoules) and K at 25 °C for the cell reaction.
A mercury battery uses the following electrode half-reactions: (c) What is the effect on the cell voltage of a tenfold change in the concentration of KOH in the electrolyte? Explain..
Zinc is attached to a ship's steel propeller to prevent the steel from rusting. Write balanced equations for the corro-sion reactions that occur (a) in the presence of Zn and (b) in the absence of Zn.