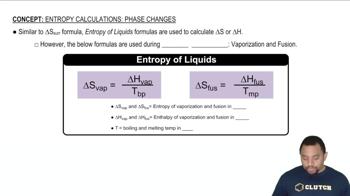
Textbook Question
Which state has higher entropy? Explain in terms of probability. (a) A perfectly ordered crystal of solid nitrous oxide or a disordered crystal in which the molecules are oriented randomly (b) Quartz glass (an amorphous solid) or a quartz crystal