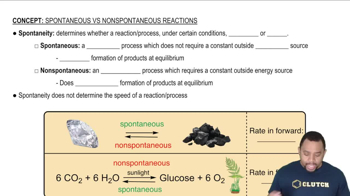
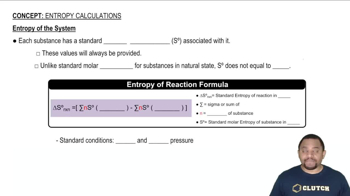
Textbook Question
What is the entropy change when the volume of 1.6 g of O2 increases from 2.5 L to 3.5 L at a constant temperature of 75 °C? Assume that O2 behaves as an ideal gas.
2
views

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.18 - Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy & Equilibrium
Ch.18 - Thermodynamics: Entropy, Free Energy & Equilibrium Problem 69
Problem 69 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance