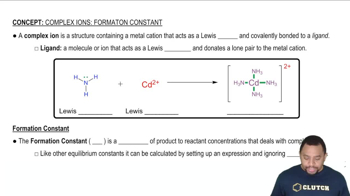
Textbook Question
Dissolution of 5.0 x 10^-3 mol of Cr(OH)3 in 1.0 L of 1.0 M NaOH gives a solution of the complex ion [Cr(OH)4]- (Kf = 8 x10^29). What fraction of the chromium in such a solution is present as uncomplexed Cr3+?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance