Textbook Question
Does the pH increase, decrease, or remain the same when the substances are added to the solutions? (a) LiF to an HF solution(b) KI to an HI solution (c) NH4Cl to an NH3 solution

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance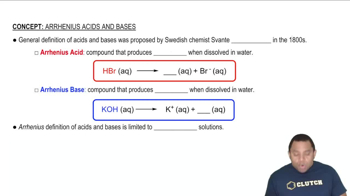


The pH of a solution of NH3 and NH4Br is 8.90. What is the molarity of NH4Br if the molarity of NH3 is 0.016 M?