Textbook Question
Ammonia 1NH32 has base dissociation constant 1Kb2 of 1.8 * 10-5. What is the concentration of an aqueous ammonia solution that has a pH of 11.68? (LO 16.11) (a) 0.28 M (b) 3.6 M (c) 9.0 * 10-3 M (d) 1.3 M
2
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance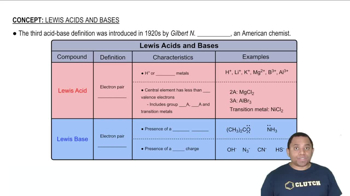


Calculate the pH of solutions prepared by:
(d) Mixing equal volumes of 0.20 M HCl and 0.50 M HNO3.
(Assume that volumes are additive.)
What is the pH and the principal source of H3O+ ions in 1.0 * 10-10 M HCl? (Hint: The pH of an acid solution can’t exceed 7.) What is the pH of 1.0 * 10-7 M HCl?