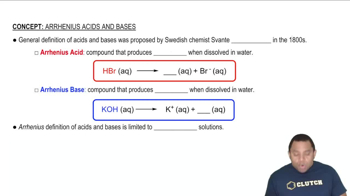
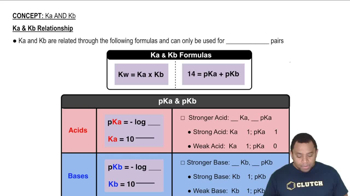
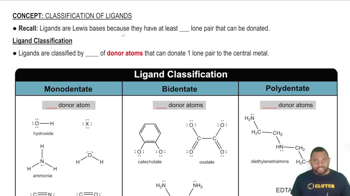
pH and Solution Classification
The pH of a solution determines whether it is acidic, basic, or neutral. A pH less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH greater than 7 is basic. By calculating the Ka for NH4+ and Kb for CN-, one can determine the dominant species in solution and thus predict the overall pH, allowing for classification of the solution.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance