Textbook Question
Look up the values of Ka in Appendix C for C6H5OH, HNO3, CH3CO2H, and HOCl, and arrange these acids in order of: (b) Decreasing percent dissociation.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
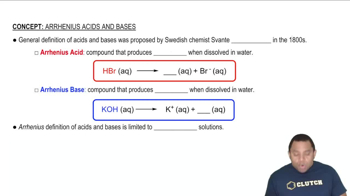

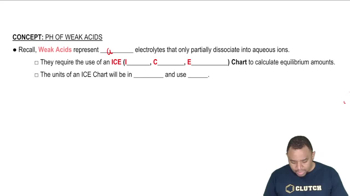
Look up the values of Ka in Appendix C for C6H5OH, HNO3, CH3CO2H, and HOCl, and arrange these acids in order of: (b) Decreasing percent dissociation.