
The reaction 2 NO1g2 + O21g2S 2 NO21g2 has the thirdorderrate law rate = k3NO423O24, where k = 25 M-2 s-1.Under the condition that 3NO4 = 2 3O24, the integratedrate law is13O242 = 8 kt +113O24022What are the concentrations of NO, O2, and NO2 after100.0 s if the initial concentrations are 3NO4 = 0.0200 Mand 3O24 = 0.0100 M?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
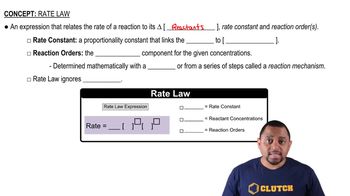
Rate Laws
Integrated Rate Laws

Stoichiometry

Some reactions are so rapid that they are said to be diffusion-controlled; that is, the reactants react as quickly as they can collide. An example is the neutralization of H3O+ by OH-, which has a second-order rate constant of 1.3⨉1011 M-1 s-1 at 25 °C. (a) If equal volumes of 2.0 M HCl and 2.0 M NaOH are mixed instantaneously, how much time is required for 99.999% of the acid to be neutralized?
Some reactions are so rapid that they are said to be diffusion-controlled; that is, the reactants react as quickly as they can collide. An example is the neutralization of H3O+ by OH-, which has a second-order rate constant of 1.3⨉1011 M-1 s-1 at 25 °C. (b) Under normal laboratory conditions, would you expect the rate of the acid–base neutralization to be limited by the rate of the reaction or by the speed of mixing?
