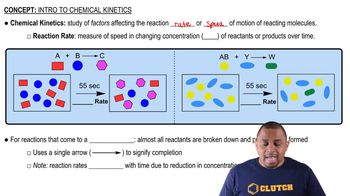
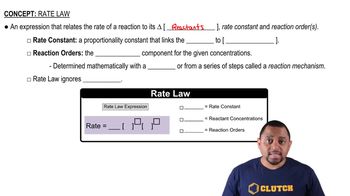
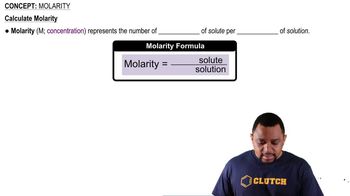
Some reactions are so rapid that they are said to be diffusion-controlled; that is, the reactants react as quickly as they can collide. An example is the neutralization of H3O+ by OH-, which has a second-order rate constant of 1.3⨉1011 M-1 s-1 at 25 °C. (a) If equal volumes of 2.0 M HCl and 2.0 M NaOH are mixed instantaneously, how much time is required for 99.999% of the acid to be neutralized?
Ch.14 - Chemical Kinetics

Chapter 14, Problem 132