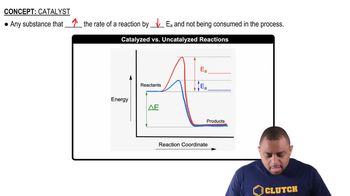
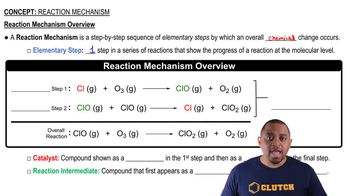
Reaction Mechanism
A reaction mechanism is a detailed description of the steps involved in a chemical reaction, including the sequence of elementary reactions. Understanding the mechanism helps in identifying catalysts and intermediates, as it outlines how reactants are transformed into products. In this case, analyzing the two given reactions will reveal the roles of various molecules throughout the process.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance