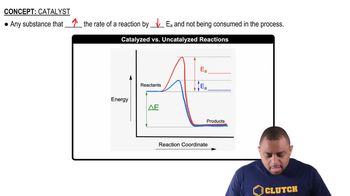
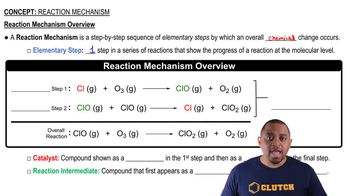
Textbook Question
Consider the following mechanism for the decomposition of nitramide 1NH2NO22 in aqueous solution: NH2NO21aq2 + OH-1aq2S NHNO2 -1aq2 + H2O1l2 NHNO2 -1aq2S N2O1g2 + OH-1aq2 (c) How will the rate of the overall reaction be affected if HCl is added to the solution?