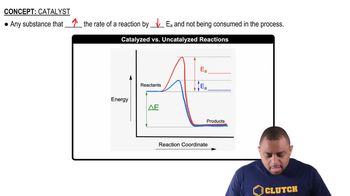
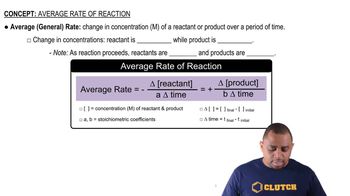
Textbook Question
Consider the reaction H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g). The reaction of a fixed amount of H2 and I2 is studied in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston. Indicate the effect of each of the following changes on the rate of the reaction. (a) An increase in temperature at constant volume