Consider the reaction H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g). The reaction of a fixed amount of H2 and I2 is studied in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston. Indicate the effect of each of the following changes on the rate of the reaction. (a) An increase in temperature at constant volume
Ch.14 - Chemical Kinetics

Chapter 14, Problem 125
Concentration–time data for the conversion of A and B to D are listed in the following table.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the rate law expression: Rate = k[X]^m[Y]^n[Z]^p[A]^q.
Compare experiments where only one reactant concentration changes while others remain constant to determine the order with respect to each reactant.
For example, compare Experiment 1 and Experiment 2 to determine the order with respect to [X].
Compare Experiment 1 and Experiment 3 to determine the order with respect to [A].
Compare Experiment 1 and Experiment 4 to determine the order with respect to [Y].

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
6mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Rate Law
The rate law is an equation that relates the rate of a chemical reaction to the concentration of its reactants. It is typically expressed in the form rate = k[A]^m[B]^n, where k is the rate constant, and m and n are the orders of the reaction with respect to reactants A and B, respectively. Understanding the rate law is crucial for predicting how changes in concentration affect the reaction rate.
Recommended video:
Guided course
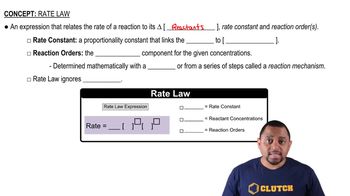
Rate Law Fundamentals
Order of Reaction
The order of a reaction refers to the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate law. It indicates how the rate of reaction is affected by the concentration of that reactant. The overall order is the sum of the individual orders, and it helps in determining the relationship between concentration and reaction rate, which is essential for analyzing experimental data.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Average Bond Order
Integrated Rate Laws
Integrated rate laws provide a mathematical relationship between the concentration of reactants and time. They are derived from the differential rate laws and can be used to determine the concentration of reactants at any given time. Understanding integrated rate laws is important for interpreting concentration-time data, such as that presented in the table, to deduce the rate law and reaction order.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rate Law Fundamentals
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Consider the reaction H2(g) + I2(g) → 2 HI(g). The reaction of a fixed amount of H2 and I2 is studied in a cylinder fitted with a movable piston. Indicate the effect of each of the following changes on the rate of the reaction. (c) The addition of a catalyst
Textbook Question
Consider the following concentration–time data for the reaction of iodide ion and hypochlorite ion (OCl-). The products are chloride ion and hypoiodite ion (OI-).
(a) Write a balanced equation for the reaction.
Textbook Question
Consider the following concentration–time data for the reaction of iodide ion and hypochlorite ion (OCl-). The products are chloride ion and hypoiodite ion (OI-).
(b) Determine the rate law, and calculate the value of the rate constant.

