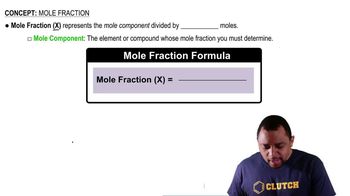
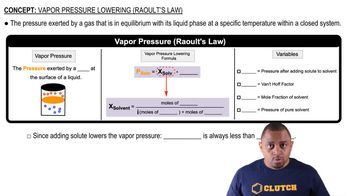
Textbook Question
Cyclopentane 1C5H102 and cyclohexane 1C6H122 are vola- tile, nonpolar hydrocarbons. At 30.0 °C, the vapor pres- sure of cyclopentane is 385 mm Hg, and the vapor pressure of cyclohexane is 122 mm Hg. What is Xpentane in a mixture of C5H10 and C6H12 that has a vapor pressure of 212 mm Hg at 30.0 °C?