Textbook Question
Residues of the herbicide atrazine (C8H14ClN5) in water can be detected at concentrations as low as 0.050 µg/L. Express this concentration of atrazine in the following units: (b) Molarity

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
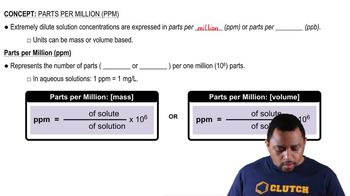


Residues of the herbicide atrazine (C8H14ClN5) in water can be detected at concentrations as low as 0.050 µg/L. Express this concentration of atrazine in the following units: (b) Molarity
How would you prepare each of the following solutions? (b) 100 mL of an aqueous solution whose K+ concentration is 0.075 M
How would you prepare 165 mL of a 0.0268 M solution of benzoic acid 1C7H6O22 in chloroform 1CHCl32?