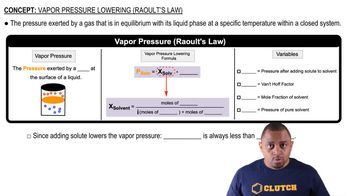
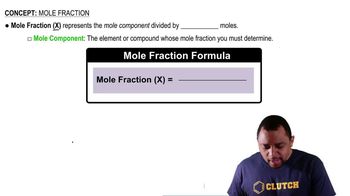
Textbook Question
There's actually much more in seawater than just dissolved NaCl. Major ions present include 19,000 ppm Cl-, 10,500 ppm Na+, 2650 ppm SO 2-, 1350 ppm Mg2+, 400 ppm Ca2+, 380 ppm K+, 140 ppm HCO3-, and 65 ppm Br-.(a) What is the total molality of all ions present in seawater?