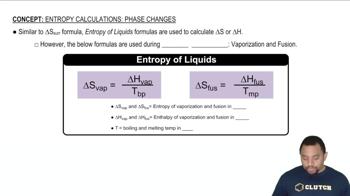
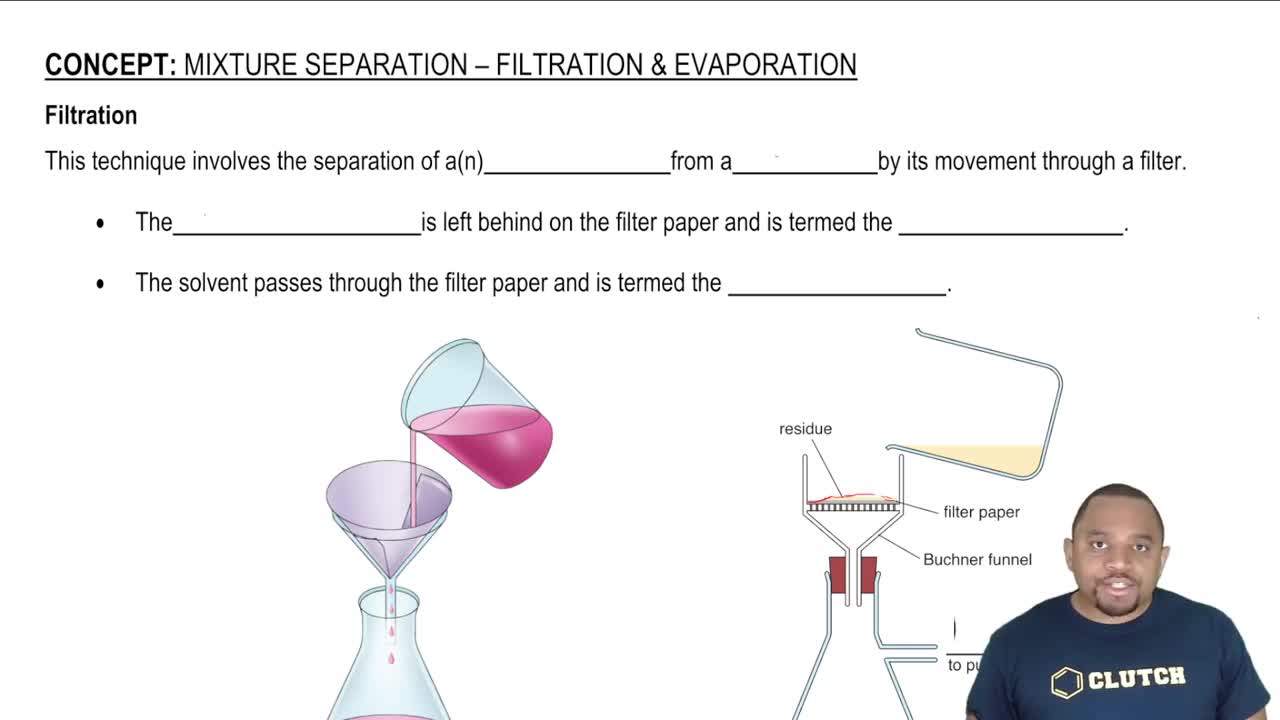
Textbook Question
How much energy in kilojoules is needed to heat 5.00 g of ice from -11.0 °C to °30.0 °C? The heat of fusion of water is 6.01 kJ>mol, and the m# olar heat capacity is 36.01 kJ>mol for ice and 75.4 J/K mol2 for liquid water

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance