Textbook Question
Naphthalene, better known as 'mothballs,' has bp = 218 °C and ΔHvap = 43.3 kJ>mol. What is the entropy of vaporization, ΔSvap in J/(K mol) for naphthalene?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
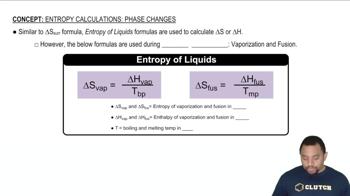
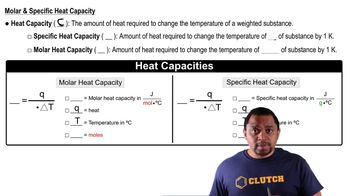
Naphthalene, better known as 'mothballs,' has bp = 218 °C and ΔHvap = 43.3 kJ>mol. What is the entropy of vaporization, ΔSvap in J/(K mol) for naphthalene?