Textbook Question
If 2.00 g of N2 gas has a volume of 0.40 L and a pressure of 6.0 atm, what is its Kelvin temperature?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
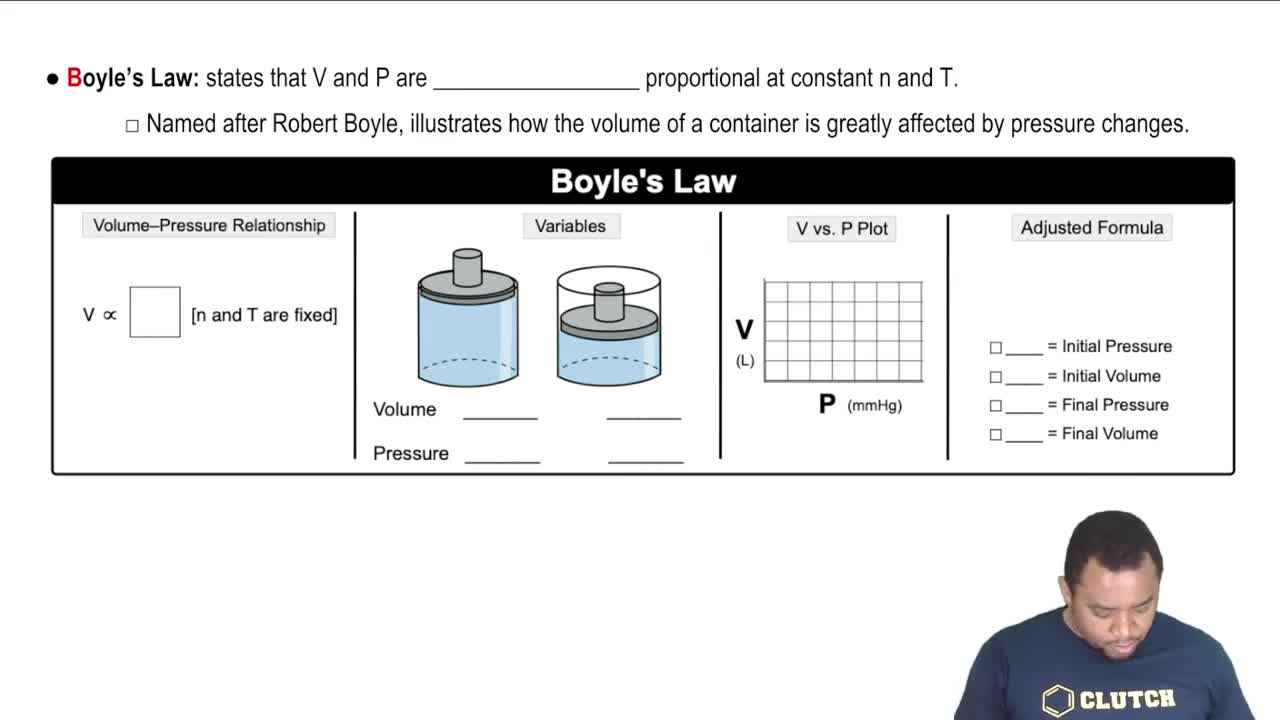
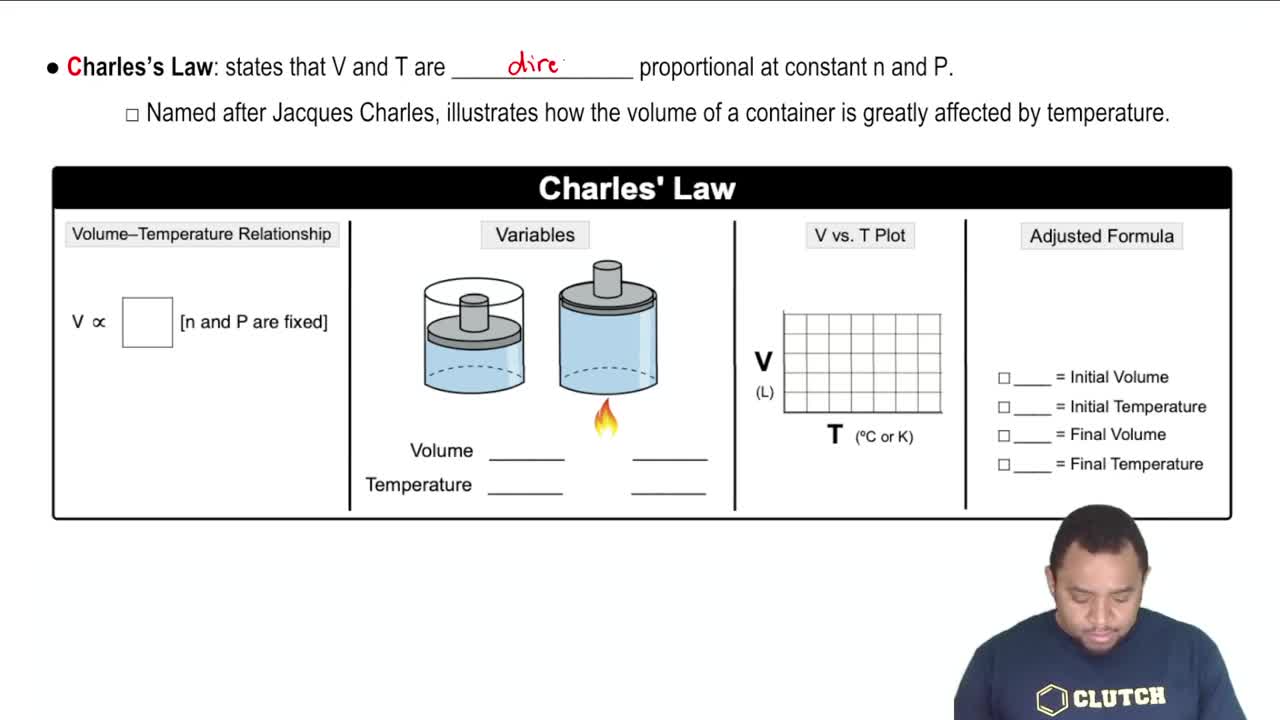
Assume that you have a cylinder with a movable piston. What would happen to the gas volume of the cylinder if you were to do the following? (d) Double the Kelvin temperature and double the pressure