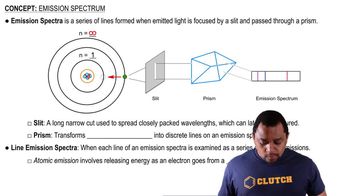
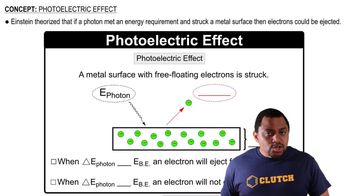
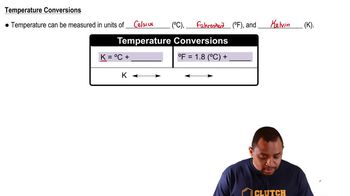
Textbook Question
The figure shows the three lowest regions of Earth's atmo- sphere.
(d) An aurora borealis is due to excitation of atoms and molecules in the atmosphere 55–95 km above Earth's surface. Which regions in the figure are involved in an aurora borealis?
4
views