Ortho-Dichlorobenzene, C6H4Cl2, is obtained when two of the adjacent hydrogen atoms in benzene are replaced with Cl atoms. A skeleton of the molecule is shown here. (b) Are there any resonance structures for the molecule? If so, sketch them.

You and a partner are asked to complete a lab entitled “Carbonates of Group 2 metal” that is scheduled to extend over two lab periods. The first lab, which is to be completed by your partner, is devoted to carrying out compositional analysis and determining the identity of the Group 2 metal (M). In the second lab, you are to determine the melting point of this compound. Upon going to the lab, you find two unlabeled vials containing white powder. You also find the following notes in your partner’s notebook—Compound 1: 40.04% M, 12.00% C, and 47.96% O (by mass); Compound 2: 69.59% M, 6.09% C, and 24.32% O (by mass). (a) What is the empirical formula for Compound 1 and the identity of M? (b) What is the empirical formula for Compound 2 and the identity of M? Upon determining the melting points of these two compounds, you find that both compounds do not melt up to the maximum temperature of your apparatus; instead, the compounds decompose and liberate a colorless gas. (c) What is the identity of the colorless gas?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
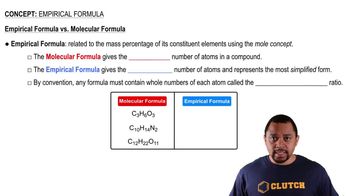
Empirical Formula
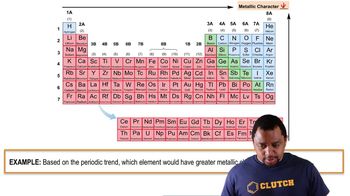
Group 2 Metals
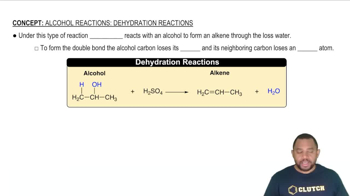
Decomposition Reactions
Two compounds are isomers if they have the same chemical formula but different arrangements of atoms. Use Table 8.3 to estimate H for each of the following gas-phase isomerization reactions and indicate which isomer has the lower enthalpy. (d) Methyl isocyanide → Acetonitrile
The electron affinity of oxygen is -141 kJ/mol, corresponding to the reaction O(g) + e- → O-(g). The lattice energy of K2O(s) is 2238 kJ/mol. Use these data along with data in Appendix C and Figure 7.11 to calculate the 'second electron affinity' of oxygen, corresponding to the reaction O-(g) + e- → O2-(g)
Under special conditions, sulfur reacts with anhydrous liquid ammonia to form a binary compound of sulfur and nitrogen. The compound is found to consist of 69.6% S and 30.4% N. Measurements of its molecular mass yield a value of 184.3 g/mol. The compound occasionally detonates on being struck or when heated rapidly. The sulfur and nitrogen atoms of the molecule are joined in a ring. All the bonds in the ring are of the same length. (a) Calculate the empirical and molecular formulas for the substance.
A common form of elemental phosphorus is the tetrahedral P4 molecule, where all four phosphorus atoms are equivalent:
(b) How many P-P bonds are there in the molecule?
