(a) As described in Section 7.7, the alkali metals react with hydrogen to form hydrides and react with halogens to form halides. Compare the roles of hydrogen and halogens in these reactions. Write balanced equations for the reaction of fluorine with calcium and for the reaction of hydrogen with calcium. (b) What is the oxidation number and electron configuration of calcium in each product?
Ch.7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 7, Problem 74a
Little is known about the properties of astatine, At, because of its rarity and high radioactivity. Nevertheless, it is possible for us to make many predictions about its properties. (a) Do you expect the element to be a gas, liquid, or solid at room temperature?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1> Consider the position of astatine (At) in the periodic table. It is located in Group 17, which is the halogen group.
insert step 2> Recall the general trend of physical states of halogens at room temperature: fluorine (F) and chlorine (Cl) are gases, bromine (Br) is a liquid, and iodine (I) is a solid.
insert step 3> Recognize that as you move down the group, the elements tend to have higher melting and boiling points due to increased molecular weight and stronger van der Waals forces.
insert step 4> Based on the trend observed in the halogen group, predict that astatine, being below iodine, is likely to be a solid at room temperature.
insert step 5> Conclude that despite the lack of experimental data, the periodic trends suggest that astatine is expected to be a solid at room temperature.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Periodic Trends
Periodic trends refer to the predictable patterns in the properties of elements as you move across or down the periodic table. For instance, elements in the same group often exhibit similar physical and chemical properties. Understanding these trends helps predict whether an element like astatine will be a gas, liquid, or solid at room temperature based on its position in the periodic table.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Periodic Trends
State of Matter
The state of matter (solid, liquid, gas) of an element at room temperature is influenced by its atomic structure and intermolecular forces. Generally, metals are solid, nonmetals can be gases or solids, and some elements are liquids. Astatine, being a halogen, is expected to be a solid due to its relatively high atomic mass and the nature of its bonding.
Recommended video:
Guided course
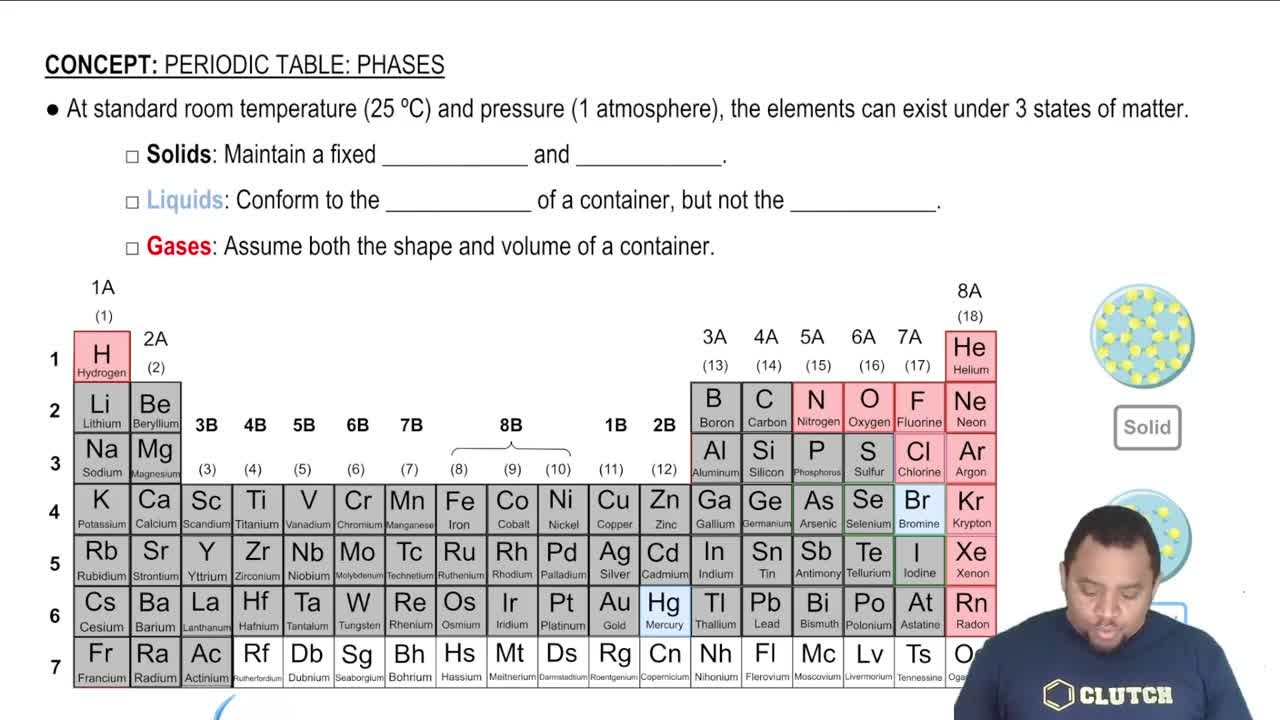
Element States of Matter
Radioactivity and Stability
Radioactivity refers to the decay of unstable atomic nuclei, which can affect the physical properties of an element. Astatine is highly radioactive, and its isotopes have short half-lives, leading to a lack of stable forms. This radioactivity can influence its state at room temperature, but predictions can still be made based on its chemical group and periodic trends.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Types of Radioactivity
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Potassium and hydrogen react to form the ionic compound potassium hydride. (b) Use data in Figures 7.10 and 7.12 to determine the energy change in kJ/mol for the following two reactions:
K(g) + H(g) → K+(g) + H-(g)
K(g) + H(g) → K-(g) + H+(g)
Textbook Question
Little is known about the properties of astatine, At, because of its rarity and high radioactivity. Nevertheless, it is possible for us to make many predictions about its properties. (b) Would you expect At to be a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Explain.
Textbook Question
Little is known about the properties of astatine, At, because of its rarity and high radioactivity. Nevertheless, it is possible for us to make many predictions about its properties. (c) What is the chemical formula of the compound it forms with Na?
