Textbook Question
Consider the isoelectronic ions F- and Na+. (d) For isoelectronic ions, how are effective nuclear charge and ionic radius related?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

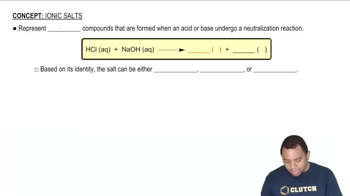

Consider the isoelectronic ions F- and Na+. (d) For isoelectronic ions, how are effective nuclear charge and ionic radius related?
Consider S, Cl, and K and their most common ions. (a) List the atoms in order of increasing size.
Arrange each of the following sets of atoms and ions in order of increasing size. Se2−,Te2−, Se
True or false? c. S2− is larger than K+.
In the ionic compounds LiF, NaCl, KBr, and RbI, the measured cation–anion distances are 2.01 Å (Li–F), 2.82 Å (Na–Cl), 3.30 Å (K–Br), and 3.67 Å (Rb–I), respectively. b. Calculate the difference between the experimentally measured ion–ion distances and the ones predicted from Figure 7.8.