The speed of sound in dry air at is 343 m/s, and the middle C on a piano keyboard has a frequency of 261 Hz. a. What is the wavelength of the sound wave corresponding to a middle C?

A popular kitchen appliance produces electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of 2450 MHz. With reference to Figure 6.4, answer the following: (a) Estimate the wavelength of this radiation.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Electromagnetic Radiation
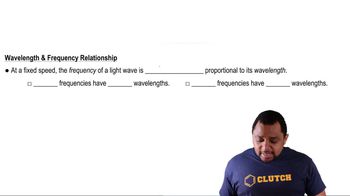
Wavelength and Frequency Relationship
Unit Conversion

The speed of sound in dry air at is 343 m/s, and the middle C on a piano keyboard has a frequency of 261 Hz. b. What would be the frequency of electromagnetic radiation with the same wavelength?
A popular kitchen appliance produces electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of 2450 MHz. With reference to Figure 6.4, answer the following: (b) Would the radiation produced by the appliance be visible to the human eye?
A popular kitchen appliance produces electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of 2450 MHz. With reference to Figure 6.4, answer the following: (c) If the radiation is not visible, do photons of this radiation have more or less energy than photons of visible light?
A popular kitchen appliance produces electromagnetic radiation with a frequency of 2450 MHz. With reference to Figure 6.4, answer the following: (d) Which of the following is the appliance likely to be? (i) A toaster oven, (ii) A microwave oven, or (iii) An electric hotplate.
