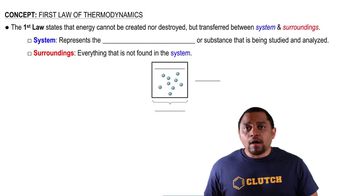
A gas is confined to a cylinder fitted with a piston and an electrical heater, as shown here:
Suppose that current is supplied to the heater so that 100 J of energy is added. Consider two different situations. In case (1) the piston is allowed to move as the energy is added. In case (2) the piston is fixed so that it cannot move. (a) In which case does the gas have the higher temperature after addition of the electrical energy?