At one time, a common means of forming small quantities of oxygen gas in the laboratory was to heat KClO3: 2 KClO3(s) → 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) ΔH = -89.4 kJ For this reaction, calculate H for the formation of (b) 10.4 g of KCl.

Consider the combustion of isopropanol, C3H7OH(l), which is the primary component of rubbing alcohol: C3H7OH(l) + 9/2 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) ΔH = -2248 kJ (b) Balance the forward reaction with whole-number coefficients. What is ΔH for the reaction represented by this equation?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Combustion Reactions
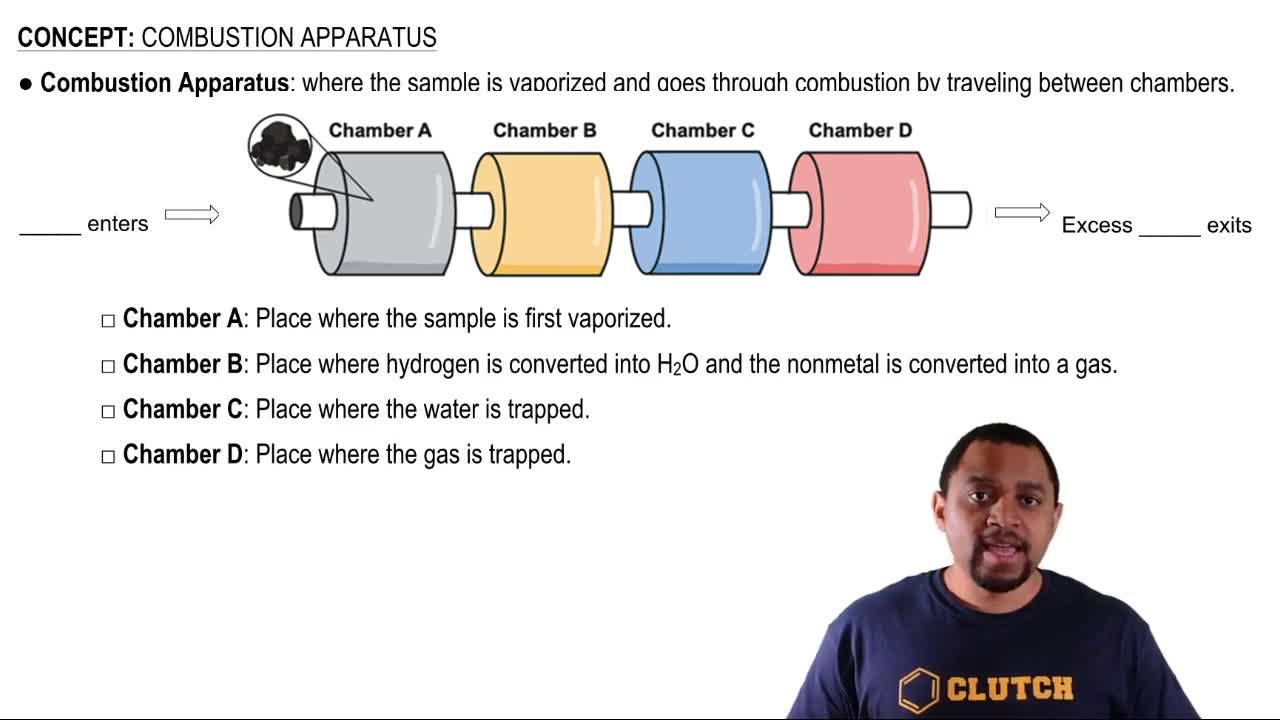
Balancing Chemical Equations

Enthalpy Change (ΔH)

At one time, a common means of forming small quantities of oxygen gas in the laboratory was to heat KClO3: 2 KClO3(s) → 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) ΔH = -89.4 kJ c. Now consider the reverse reaction, in which KClO3 is formed from KCl and O2. What is Δ𝐻 for the formation of 19.1 g KClO3 from KCl and O2?
Consider the combustion of isopropanol, C3H7OH(l), which is the primary component of rubbing alcohol: C3H7OH(l) + 9/2 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) ΔH = -2248 kJ a. What is the enthalpy change for the reverse reaction?
Consider the decomposition of liquid benzene, C6H6(l), to gaseous acetylene, C2H2(g): C6H6(l) → 3 C2H2(g) ΔH = +630 kJ (a) What is the enthalpy change for the reverse reaction?
Consider the decomposition of liquid benzene, C6H6(l), to gaseous acetylene, C2H2(g): C6H6(l) → 3 C2H2(g) ΔH = +630 kJ (b) What is H for the formation of 1 mol of acetylene?
Consider the decomposition of liquid benzene, C6H6(l), to gaseous acetylene, C2H2(g): C6H6(l) → 3 C2H2(g) ΔH = +630 kJ (c) Which is more likely to be thermodynamically favored, the forward reaction or the reverse reaction?
