Textbook Question
In the accompanying cylinder diagram, a chemical process occurs at constant temperature and pressure. (a) Is the sign of w indicated by this change positive or negative?
2
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

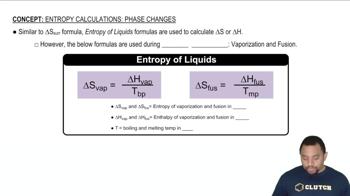
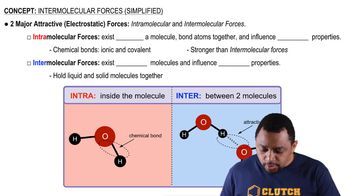
In the accompanying cylinder diagram, a chemical process occurs at constant temperature and pressure. (a) Is the sign of w indicated by this change positive or negative?
Consider the two diagrams that follow. (d) Would similar relationships hold for the work involved in each process?
(a) What is the electrostatic potential energy (in joules) between two electrons that are separated by 62 pm?
(b) What is the change in potential energy if the distance separating the two electrons is increased to 1.0 nm?