Write the balanced molecular and net ionic equations for each of the following neutralization reactions: (b) Solid chromium(III) hydroxide reacts with nitrous acid.
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 4, Problem 42a,b
Because the oxide ion is basic, metal oxides react readily with acids. (a) Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: FeO(s) + 2 HClO4(aq) → Fe(ClO4)2(aq) + H2O(l) (b) Based on the equation in part (a), write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs between NiO(s) and an aqueous solution of nitric acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the reactants: Nickel(II) oxide (NiO) and nitric acid (HNO₃).
Write the balanced molecular equation for the reaction: NiO(s) + 2HNO₃(aq) → Ni(NO₃)₂(aq) + H₂O(l).
Determine the ions present in the aqueous solution: H⁺ and NO₃⁻ from HNO₃, and Ni²⁺ and NO₃⁻ from Ni(NO₃)₂.
Identify the spectator ions: NO₃⁻ ions are present on both sides of the equation and do not participate in the reaction.
Write the net ionic equation by removing the spectator ions: NiO(s) + 2H⁺(aq) → Ni²⁺(aq) + H₂O(l).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
7mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons (H+) between reactants. In this context, metal oxides, which are basic, react with acids to form water and a salt. Understanding the nature of acids and bases, as defined by the Brønsted-Lowry theory, is crucial for predicting the products of such reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid-Base Reaction
Net Ionic Equations
A net ionic equation represents the actual chemical species that are involved in a reaction, excluding spectator ions that do not participate. To write a net ionic equation, one must first identify the reactants and products, then eliminate ions that appear unchanged on both sides of the equation, focusing on the species that undergo a change.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Net Ionic Equations
Metal Oxides
Metal oxides are compounds formed by the reaction of metals with oxygen, typically exhibiting basic properties. When metal oxides like NiO react with acids, they neutralize the acid, leading to the formation of water and a corresponding salt. Recognizing the behavior of metal oxides in acid-base chemistry is essential for understanding their reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
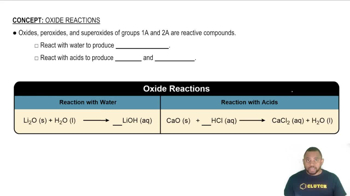
Oxide Reactions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Write the balanced molecular and net ionic equations for each of the following neutralization reactions: (c) Aqueous nitric acid and aqueous ammonia react.
Textbook Question
Write balanced molecular and net ionic equations for the following reactions, and identify the gas formed in each: (a) solid cadmium sulfide reacts with an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid (b) solid magnesium carbonate reacts with an aqueous solution of perchloric acid.
Textbook Question
True or false: a. If a substance is oxidized, it is gaining electrons.
Textbook Question
(a) Which region of the periodic table shown here contains elements that are easiest to oxidize? (b) Which region contains the least readily oxidized elements?
