Write the balanced molecular and net ionic equations for each of the following neutralization reactions: (c) Aqueous nitric acid and aqueous ammonia react.

As K2O dissolves in water, the oxide ion reacts with water molecules to form hydroxide ions. (a) Write the molecular and net ionic equations for this reaction. (b) Based on the definitions of acid and base, what ion is the base in this reaction? (c) What is the acid in the reaction? (d) What is the spectator ion in the reaction?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Dissociation and Ion Formation
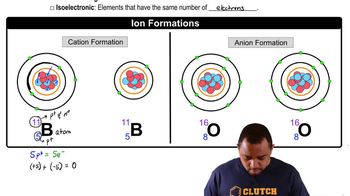
Acid-Base Theory

Net Ionic Equations

Write balanced molecular and net ionic equations for the following reactions, and identify the gas formed in each: (a) solid cadmium sulfide reacts with an aqueous solution of sulfuric acid (b) solid magnesium carbonate reacts with an aqueous solution of perchloric acid.
Because the oxide ion is basic, metal oxides react readily with acids. (a) Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: FeO(s) + 2 HClO4(aq) → Fe(ClO4)2(aq) + H2O(l) (b) Based on the equation in part (a), write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs between NiO(s) and an aqueous solution of nitric acid.
True or false: a. If a substance is oxidized, it is gaining electrons.
(a) Which region of the periodic table shown here contains elements that are easiest to oxidize? (b) Which region contains the least readily oxidized elements?
Determine the oxidation number of sulfur in each of the following substances: (a) barium sulfate, BaSO4 (b) sulfurous acid, H2SO3 (c) strontium sulfide, SrS
