A sample of the male sex hormone testosterone, C19H28O2, contains 3.88×1021 hydrogen atoms. (b) How many molecules of testosterone does it contain?
Ch.3 - Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 45a
Give the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample contains a.0.0130 mol C, 0.0390 mol H, and 0.0065 mol O
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the number of moles of each element in the compound: 0.0130 mol C, 0.0390 mol H, and 0.0065 mol O.
Divide the number of moles of each element by the smallest number of moles present among the elements to find the simplest whole number ratio. In this case, divide each by 0.0065 mol.
Calculate the resulting ratios: \( \frac{0.0130}{0.0065} \) for C, \( \frac{0.0390}{0.0065} \) for H, and \( \frac{0.0065}{0.0065} \) for O.
Round the ratios to the nearest whole number to determine the subscripts for each element in the empirical formula.
Write the empirical formula using the whole number ratios as subscripts for each element.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
51sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Empirical Formula
The empirical formula of a compound represents the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements present in that compound. It is derived from the mole quantities of each element, providing a basic understanding of the composition without indicating the actual number of atoms in a molecule.
Recommended video:
Guided course
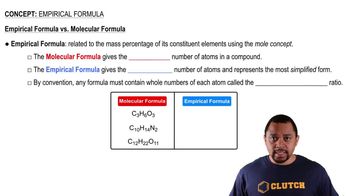
Empirical vs Molecular Formula
Mole Concept
The mole is a fundamental unit in chemistry that quantifies the amount of substance. One mole corresponds to approximately 6.022 x 10²³ entities (atoms, molecules, etc.). Understanding the mole concept is essential for converting between mass, number of particles, and volume in chemical calculations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mole Concept
Mole Ratio
Mole ratio is the ratio of the number of moles of one substance to the number of moles of another substance in a chemical reaction or mixture. It is crucial for determining the empirical formula, as it allows for the simplification of the mole quantities of each element to their smallest whole-number ratio.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Neutron-Proton Ratio
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The allowable concentration level of vinyl chloride, C2H3Cl, in the atmosphere in a chemical plant is 2.0×10−6 g/L. How many moles of vinyl chloride in each liter does this represent?
Textbook Question
At least 25 mg of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active ingredient in marijuana, is required to produce intoxication. The molecular formula of THC is C21H30O2. How many molecules?
Textbook Question
Give the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample contains b.11.66 g iron and 5.01 g oxygen
Textbook Question
Give the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample contains c.40.0% C, 6.7% H, and 53.3% O by mass.
Textbook Question
Determine the empirical formula of each of the following compounds if a sample contains a. 0.104 mol K, 0.052 mol C, and 0.156 mol O;
