Ch.23 - Transition Metals and Coordination Chemistry

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 23, Problem 37
Complete the exercises below. Write the names of the following compounds, using the standard nomenclature rules for coordination complexes: d. [Pt(H₂O)₄(C₂O₄)]Br₂
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the central metal atom in the coordination complex, which is platinum (Pt) in this case.
Determine the oxidation state of the central metal. The complex is neutral overall, and the charge of the oxalate ligand (C₂O₄) is -2. Since there are two bromide ions (Br⁻) outside the coordination sphere, the oxidation state of Pt can be calculated.
List the ligands in alphabetical order. Here, the ligands are water (H₂O) and oxalate (C₂O₄). Water is a neutral ligand, and oxalate is a bidentate ligand with a -2 charge.
Name the ligands: 'aqua' for water and 'oxalato' for oxalate. Since there are four water molecules, use the prefix 'tetra' for 'tetra-aqua'.
Combine the names: Start with the ligands in alphabetical order followed by the metal with its oxidation state in Roman numerals. The name of the complex is 'tetra-aqua-oxalato-platinum(II) bromide'.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Coordination Complexes
Coordination complexes consist of a central metal atom or ion bonded to surrounding molecules or ions, known as ligands. The arrangement and type of ligands influence the properties and reactivity of the complex. Understanding the structure of coordination complexes is essential for naming them correctly.
Recommended video:
Guided course
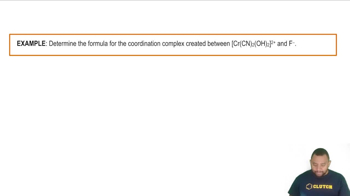
Coordination Complexes Example
Nomenclature of Coordination Compounds
The nomenclature of coordination compounds follows specific rules established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). This includes naming the ligands first, followed by the metal, and indicating the oxidation state of the metal in Roman numerals. The overall charge of the complex also affects the naming of the counterions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
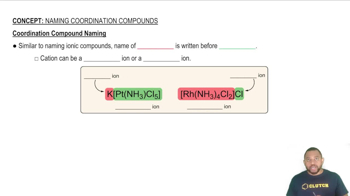
Coordination Compound Naming
Ligands and Their Types
Ligands are ions or molecules that donate electron pairs to the central metal atom in a coordination complex. They can be classified as monodentate (binding through one atom), bidentate (binding through two atoms), or polydentate (binding through multiple atoms). The nature and number of ligands play a crucial role in determining the stability and geometry of the complex.
Recommended video:
Guided course
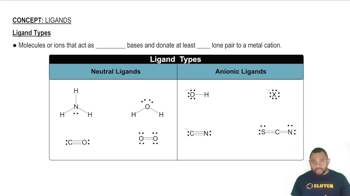
Ligand Types
Related Practice
