Ch.22 - Chemistry of the Nonmetals

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 22, Problem 47
Complete the exercises below. Write a balanced equation for each of the following reactions: a. Sulfur dioxide reacts with water. b. Solid zinc sulfide reacts with hydrochloric acid. c. Elemental sulfur reacts with sulfite ion to form thiosulfate. d. Sulfur trioxide is dissolved in sulfuric acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the reactants and products for each reaction. For example, in reaction (a), the reactants are sulfur dioxide (SO_2) and water (H_2O), and the product is sulfurous acid (H_2SO_3).
Write the unbalanced chemical equation for each reaction. For reaction (a), it would be: SO_2 + H_2O → H_2SO_3.
Balance the chemical equation by ensuring the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. For reaction (a), the equation is already balanced: SO_2 + H_2O → H_2SO_3.
Repeat the process for reaction (b): Identify reactants (ZnS and HCl) and products (ZnCl_2 and H_2S), write the unbalanced equation: ZnS + HCl → ZnCl_2 + H_2S, and balance it.
Continue with reactions (c) and (d) by identifying reactants and products, writing unbalanced equations, and balancing them. For example, for reaction (c), the unbalanced equation is S + SO_3^{2-} → S_2O_3^{2-}.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations involves ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides. This is based on the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. To balance an equation, coefficients are adjusted in front of the chemical formulas.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Types of Chemical Reactions
Understanding the types of chemical reactions is crucial for predicting products and writing balanced equations. Common types include synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement reactions. Recognizing the type of reaction helps in determining the appropriate reactants and products involved.
Recommended video:
Guided course
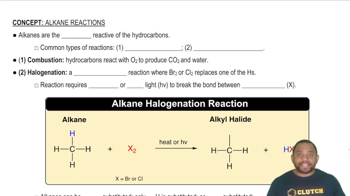
Common Types of Alkane Reactions
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of protons (H+) between reactants. In these reactions, acids donate protons while bases accept them. Recognizing the role of acids and bases in a reaction is essential for writing balanced equations, especially when dealing with reactions involving strong acids like hydrochloric acid and their interactions with sulfides.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Acid-Base Reaction
Related Practice
