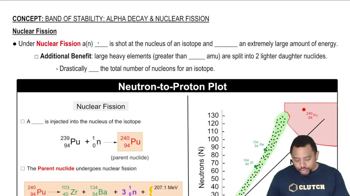
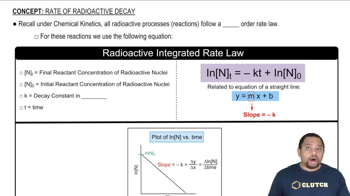
Textbook Question
Despite the similarities in the chemical reactivity of elements in the lanthanide series, their abundances in Earth's crust vary by two orders of magnitude. This graph shows the relative abundance as a function of atomic number. Which of the following statements best explains the sawtooth variation across the series? (a) The elements with an odd atomic number lie above the belt of stability. (b) The elements with an odd atomic number lie below the belt of stability. (c) The elements with an even atomic number have a magic number of protons. (d) Pairs of protons have a special stability.
2
views