A disproportionation reaction is an oxidation–reduction reaction in which the same substance is oxidized and reduced. Complete and balance the following disproportionation reactions:
(b) MnO42-(aq) → MnO4-(aq) + MnO2(s) (acidic solution)

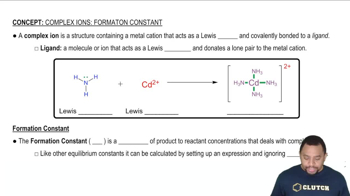
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


A disproportionation reaction is an oxidation–reduction reaction in which the same substance is oxidized and reduced. Complete and balance the following disproportionation reactions:
(b) MnO42-(aq) → MnO4-(aq) + MnO2(s) (acidic solution)
Predict whether the following reactions will be spontaneous in acidic solution under standard conditions: (a) oxidation of Sn to Sn2+ by I2 (to form I-), (b) reduction of Ni2+ to Ni by I- (to form I2), (c) reduction of Ce4+ to Ce3+ by H2O2, (d) reduction of Cu2+ to Cu by Sn2+ (to form Sn4+).
A voltaic cell is constructed that uses the following half-cell reactions:
Cu+(aq) + e- → Cu(s)
I2(s) + 2 e- → 2 I-(aq)
The cell is operated at 298 K with [Cu+] = 0.25 M and [I-] = 0.035 M.
(a) Determine E for the cell at these concentrations.