(a) Calculate the mass of Li formed by electrolysis of molten LiCl by a current of 7.5 × 104 A flowing for a period of 24 h. Assume the electrolytic cell is 85% efficient. (b) What is the minimum voltage required to drive the reaction?

A disproportionation reaction is an oxidation–reduction reaction in which the same substance is oxidized and reduced. Complete and balance the following disproportionation reactions:
(b) MnO42-(aq) → MnO4-(aq) + MnO2(s) (acidic solution)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
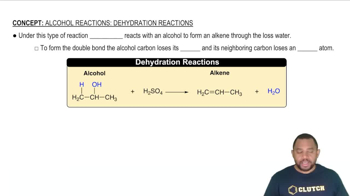
Disproportionation Reaction
Oxidation States

Balancing Redox Reactions

Predict whether the following reactions will be spontaneous in acidic solution under standard conditions: (a) oxidation of Sn to Sn2+ by I2 (to form I-), (b) reduction of Ni2+ to Ni by I- (to form I2), (c) reduction of Ce4+ to Ce3+ by H2O2, (d) reduction of Cu2+ to Cu by Sn2+ (to form Sn4+).
Gold exists in two common positive oxidation states, +1 and +3. The standard reduction potentials for these oxidation states are Au+1aq2 + e- ¡ Au1s2 Ered ° = +1.69 V Au3+1aq2 + 3 e- ¡ Au1s2 Ered ° = +1.50 V (c) Miners obtain gold by soaking gold-containing ores in an aqueous solution of sodium cyanide. A very soluble complex ion of gold forms in the aqueous solution because of the redox reaction 4 Au1s2 + 8 NaCN1aq2 + 2 H2O1l2 + O21g2 ¡ 4 Na3Au1CN2241aq2 + 4 NaOH1aq2 What is being oxidized, and what is being reduced in this reaction?
