Two substances have the same molecular and empirical formulas. Does this mean that they must be the same compound?
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 49c
Write the empirical formula corresponding to each of the following molecular formulas: (c) C4H8O2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the subscripts in the molecular formula C₄H₈O₂.
Divide each subscript in the molecular formula by the GCD to simplify the ratio of atoms.
Write the empirical formula using the simplified ratio of atoms obtained from the previous step.
Ensure that the empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of the elements present in the compound.
Verify that the empirical formula cannot be further simplified by checking if the subscripts have any common factors other than 1.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Empirical Formula
The empirical formula represents the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound. It is derived from the molecular formula by dividing the subscripts of each element by their greatest common divisor. For example, the empirical formula of C4H8O2 is C2H4O, indicating that for every two carbon atoms, there are four hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Recommended video:
Guided course
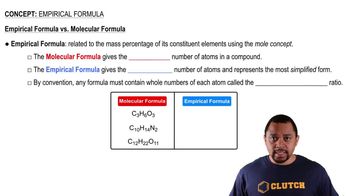
Empirical vs Molecular Formula
Molecular Formula
The molecular formula provides the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a compound. It can be the same as the empirical formula or a multiple of it. In the case of C4H8O2, the molecular formula indicates that there are four carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms, and two oxygen atoms in each molecule, which can be simplified to its empirical form.
Recommended video:
Guided course
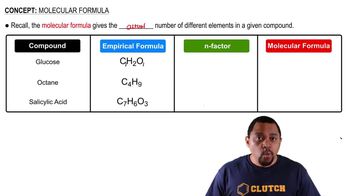
Determining Molecular Formulas
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The greatest common divisor is the largest integer that divides the subscripts of the elements in a molecular formula without leaving a remainder. It is essential for simplifying the molecular formula to its empirical form. For C4H8O2, the GCD of the subscripts 4, 8, and 2 is 2, which is used to reduce the formula to C2H4O.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Common Ion Effect
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Write the empirical formula corresponding to each of the following molecular formulas: (a) Al2Br6
Textbook Question
Write the empirical formula corresponding to each of the following molecular formulas: (b) C8H10
Textbook Question
Write the empirical formula corresponding to each of the following molecular formulas: (d) P4O10 (e) C6H4Cl2 (f) B3N3H6.
Textbook Question
Determine the molecular and empirical formulas of the following: (a) the organic solvent benzene, which has six carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms
Textbook Question
Determine the molecular and empirical formulas of the following: (b) the compound silicon tetrachloride, which has a silicon atom and four chlorine atoms and is used in the manufacture of computer chips
1
views
1
rank
