You are asked to prepare a pH = 3.00 buffer solution starting from 1.25 L of a 1.00 M solution of hydrofluoric acid (HF) and any amount you need of sodium fluoride (NaF). (b) How many grams of sodium fluoride should be added to prepare the buffer solution? Neglect the small volume change that occurs when the sodium fluoride is added.
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 25a
You are asked to prepare a pH = 3.00 buffer solution starting from 1.25 L of a 1.00 M solution of hydrofluoric acid (HF) and any amount you need of sodium fluoride (NaF). (a) What is the pH of the hydrofluoric acid solution prior to adding sodium fluoride?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the chemical species involved: Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a weak acid, and its dissociation in water can be represented as: \( \text{HF} \rightleftharpoons \text{H}^+ + \text{F}^- \).
Use the acid dissociation constant (\( K_a \)) for HF to set up the equilibrium expression: \( K_a = \frac{[\text{H}^+][\text{F}^-]}{[\text{HF}]} \).
Look up the \( K_a \) value for HF, which is typically around \( 6.8 \times 10^{-4} \).
Assume that the initial concentration of HF is 1.00 M and that the change in concentration due to dissociation is \( x \). Set up the expression: \( K_a = \frac{x^2}{1.00 - x} \).
Solve for \( x \), which represents the \([\text{H}^+]\) concentration, and then calculate the pH using the formula: \( \text{pH} = -\log[\text{H}^+] \).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
9mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and Acid-Base Chemistry
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, indicating its acidity or basicity. A pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic. Understanding pH is crucial for analyzing solutions, especially in buffer systems where the pH remains relatively stable despite the addition of acids or bases.
Recommended video:
Guided course
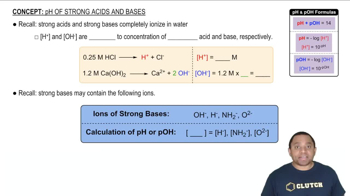
pH of Strong Acids and Bases
Weak Acids and Their Dissociation
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) is a weak acid that partially dissociates in water to produce hydrogen ions (H⁺) and fluoride ions (F⁻). The degree of dissociation is characterized by the acid dissociation constant (Ka), which helps determine the concentration of H⁺ ions in the solution and thus the pH. This concept is essential for calculating the pH of the HF solution before any buffer components are added.
Recommended video:
Guided course
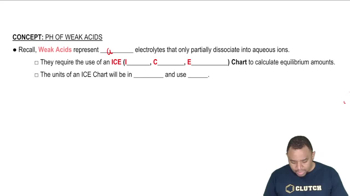
ICE Charts of Weak Acids
Buffer Solutions
A buffer solution is a system that resists changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acids or bases. It typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base, which in this case is HF and NaF. Understanding how buffers work is important for preparing solutions with specific pH values, as they maintain stability in pH during chemical reactions or external changes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Buffer Solutions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
You are asked to prepare a pH = 4.00 buffer starting from 1.50 L of 0.0200 M solution of benzoic acid 1C6H5COOH2 and any amount you need of sodium benzoate 1C6H5COONa2. (a) What is the pH of the benzoic acid solution prior to adding sodium benzoate?
Textbook Question
You are asked to prepare a pH = 4.00 buffer starting from 1.50 L of 0.0200 M solution of benzoic acid 1C6H5COOH2 and any amount you need of sodium benzoate 1C6H5COONa2. (b) How many grams of sodium benzoate should be added to prepare the buffer? Neglect the small volume change that occurs when the sodium benzoate is added.
