Indicate whether each of the following statements is correct or incorrect. (c) Conjugate acids of weak bases produce more acidic solutions than conjugate acids of strong bases.
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 101
Which, if any, of the following statements are true? (a) The stronger the base, the smaller the pKb. (b) The stronger the base, the larger the pKb. (c) The stronger the base, the smaller the Kb. (d) The stronger the base, the larger the Kb. (e) The stronger the base, the smaller the pKa of its conjugate acid. (f) The stronger the base, the larger the pKa of its conjugate acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the relationship between base strength and Kb: A stronger base has a larger Kb value because it dissociates more in solution, increasing the concentration of OH⁻ ions.
Relate Kb to pKb: pKb is the negative logarithm of Kb (pKb = -log(Kb)). Therefore, a larger Kb results in a smaller pKb.
Analyze statement (a): 'The stronger the base, the smaller the pKb.' This is true because a stronger base has a larger Kb, leading to a smaller pKb.
Analyze statement (b): 'The stronger the base, the larger the pKb.' This is false because a stronger base has a larger Kb, which results in a smaller pKb.
Consider the relationship between a base and its conjugate acid: A stronger base has a weaker conjugate acid, which means the conjugate acid has a larger pKa. Therefore, statement (f) is true.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Base Strength and pKb
The strength of a base is inversely related to its pKb value. A stronger base has a lower pKb, indicating a greater tendency to accept protons. This relationship is crucial for understanding how bases behave in chemical reactions and how their strength can be quantified.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Strength of Conjugate Acids and Bases
Base Strength and Kb
The base dissociation constant (Kb) measures the strength of a base in solution. A stronger base corresponds to a larger Kb value, reflecting its ability to dissociate and produce hydroxide ions. This concept is essential for comparing the relative strengths of different bases.
Recommended video:
Guided course
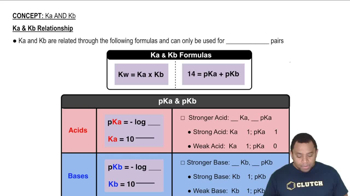
Ka and Kb Relationship
Conjugate Acids and pKa
The pKa of a conjugate acid is a measure of its acidity, with lower pKa values indicating stronger acids. For a stronger base, the pKa of its conjugate acid will be smaller, as stronger bases correspond to weaker conjugate acids. Understanding this relationship helps in predicting the behavior of acids and bases in chemical equilibria.
Recommended video:
Guided course
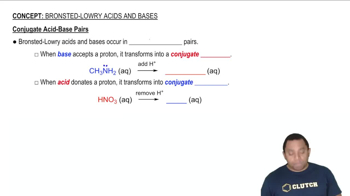
Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Indicate whether each of the following statements is correct or incorrect. (d) K+ ion is acidic in water because it causes hydrating water molecules to become more acidic.
Textbook Question
A solution is made by adding 0.300 g Ca1OH221s2, 50.0 mL of 1.40 M HNO3, and enough water to make a final volume of 75.0 mL. Assuming that all of the solid dissolves, what is the pH of the final solution?
Textbook Question
Predict how each molecule or ion would act, in the Brønsted-Lowry sense, in aqueous solution by writing 'acid,' 'base,' 'both,' or 'neither' on the line provided. (b) Prozac
Textbook Question
Calculate the pH of a solution made by adding 2.50 g of lithium oxide 1Li2O2 to enough water to make 1.500 L of solution.
