Textbook Question
Calculate Kb values for CH3COO- and ClO-.
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance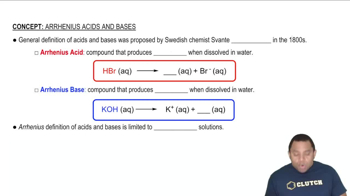


Calculate Kb values for CH3COO- and ClO-.
Given that Kb for ammonia is 1.8 × 10-5 and that for hydroxylamine is 1.1 × 10-8, which is the stronger base?
Which is the stronger acid, the ammonium ion or the hydroxylammonium ion?
Using data from Appendix D, calculate 3OH-4 and pH for each of the following solutions: (b) 0.035 M Na2S
Pyridinium bromide 1C5H5NHBr2 is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into C5H5NH+ and Br-. An aqueous solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. (a) Write out the reaction that leads to this acidic pH.