Calculate [H+] for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) [OH-] = 0.00045 M (b) [OH-] = 8.8 × 10-9 M (c) a solution in which [OH-] is 100 times greater than [H+].
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 34c
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (c) a solution in which 3H+4 is 1000 times greater than 3OH-4.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the relationship between \([H^+]\) and \([OH^-]\) in the solution. Given that \([H^+]\) is 1000 times greater than \([OH^-]\), express this as \([H^+] = 1000 \times [OH^-]\).
Recall the water dissociation constant at 25°C: \(K_w = [H^+][OH^-] = 1.0 \times 10^{-14}\).
Substitute \([H^+] = 1000 \times [OH^-]\) into the expression for \(K_w\): \((1000 \times [OH^-]) \times [OH^-] = 1.0 \times 10^{-14}\).
Solve for \([OH^-]\) by simplifying the equation: \(1000 \times [OH^-]^2 = 1.0 \times 10^{-14}\).
Determine the nature of the solution by comparing \([H^+]\) and \([OH^-]\). If \([H^+] > [OH^-]\), the solution is acidic.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and pOH
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, while pOH measures the hydroxide ion concentration. The relationship between pH and pOH is defined by the equation pH + pOH = 14 at 25°C. A solution is considered acidic if pH < 7, basic if pH > 7, and neutral if pH = 7.
Recommended video:
Guided course
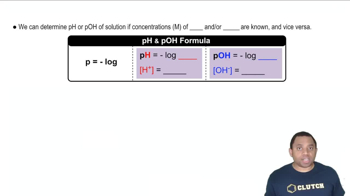
pH and pOH Calculations
Ion Concentration Ratio
The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution determines its acidity or basicity. If the concentration of H+ is significantly greater than that of OH-, the solution is acidic. Conversely, if OH- is more concentrated, the solution is basic. In this case, the problem states that [H+] is 1000 times greater than [OH-], indicating an acidic solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Neutron-Proton Ratio
Logarithmic Scale of pH
The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning each whole number change on the scale represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion concentration. Therefore, a solution with [H+] that is 1000 times greater than [OH-] corresponds to a pH of approximately 3, indicating a strongly acidic solution. Understanding this scale is crucial for interpreting the acidity or basicity of solutions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The pH Scale
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) 3H+4 = 0.0505 M
Textbook Question
Calculate 3OH-4 for each of the following solutions, and indicate whether the solution is acidic, basic, or neutral: (b) 3H+4 = 2.5 * 10-10 M
Textbook Question
Deuterium oxide 1D2O, where D is deuterium, the hydrogen-2 isotope) has an ion-product constant, Kw, of 8.9 * 10-16 at 20 °C. Calculate 3D+4 and 3OD-4 for pure (neutral) D2O at this temperature.
Textbook Question
By what factor does [H+] change for a pH change of (a) 2.00 units? (b) 0.50 units?
