A mixture of 0.2000 mol of CO2, 0.1000 mol of H2, and 0.1600 mol of H2O is placed in a 2.000-L vessel. The following equilibrium is established at 500 K: CO2(g) + H2(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2O(g) (d) Calculate Kc for the reaction.

Two different proteins X and Y are dissolved in aqueous solution at 37 _x001F_C. The proteins bind in a 1:1 ratio to form XY. A solution that is initially 1.00 mM in each protein is allowed to reach equilibrium. At equilibrium, 0.20 mM of free X and 0.20 mM of free Y remain. What is Kc for the reaction?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Equilibrium Constant (Kc)

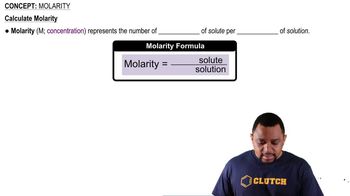
Molarity and Concentration
Stoichiometry of the Reaction

Indicate whether each of the following statements about the reaction quotient Q is true or false: (a) The expression for 𝑄𝑐 looks the same as the expression for 𝐾𝑐.
Indicate whether each of the following statements about the reaction quotient Q is true or false: (b) If 𝑄𝑐 < 𝐾𝑐, the reaction needs to proceed to the right to reach equilibrium.
At 100°C, the equilibrium constant for the reaction COCl2(𝑔) ⇌ CO(𝑔) + Cl2(𝑔) has the value 𝐾𝑐 = 2.19×10−10. Are the following mixtures of COCl2, CO, and Cl2 at 100°C at equilibrium? If not, indicate the direction that the reaction must proceed to achieve equilibrium.
(a) [COCl2] = 2.00×10−3 M, [CO] = 3.3×10−6 M, [Cl2] = 6.62×10−6 M
(b) [COCl2] = 4.50×10−2 M, [CO] = 1.1×10−7 M, [Cl2] = 2.25×10−6 M
(c) [COCl2] = 0.0100 M, [CO] = [Cl2] = 1.48×10−6 M
