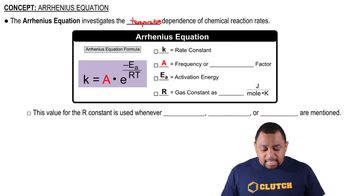
Textbook Question
Based on their activation energies and energy changes and assuming that all collision factors are the same, rank the following reactions from slowest to fastest. (a) Ea = 45 kJ>mol; E = -25 kJ>mol (b) Ea = 35 kJ>mol; E = -10 kJ>mol (c) Ea = 55 kJ>mol; E = 10 kJ>mol