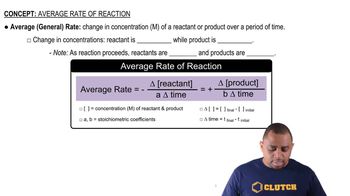
The isomerization of methyl isonitrile (CH3NC) to acetonitrile (CH3CN) was studied in the gas phase at 215°C, and the following data were obtained:
Time (s) [CH3NC] (M)
0 0.0165
2000 0.0110
5000 0.00591
8000 0.00314
12,000 0.00137
15,000 0.00074
(b) Calculate the average rate of reaction over the entire time of the data from t = 0 to t = 15,000 s.