Consider the following hypothetical aqueous reaction: A(aq) → B(aq). A flask is charged with 0.065 mol of A in a total volume of 100.0 mL. The following data are collected: Time (min) 0 10 20 30 40 Moles of A 0.065 0.051 0.042 0.036 0.031 (c) Between t = 10 min and t = 30 min, what is the average rate of appearance of B in units of M/s? Assume that the volume of the solution is constant.

The isomerization of methyl isonitrile (CH3NC) to acetonitrile (CH3CN) was studied in the gas phase at 215°C, and the following data were obtained:
Time (s) [CH3NC] (M)
0 0.0165
2000 0.0110
5000 0.00591
8000 0.00314
12,000 0.00137
15,000 0.00074
(b) Calculate the average rate of reaction over the entire time of the data from t = 0 to t = 15,000 s.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Reaction Rate
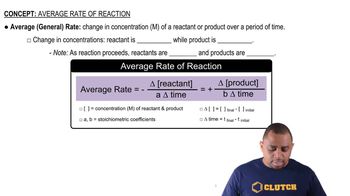
Concentration Change

Average Rate Calculation

A flask is charged with 0.100 mol of A and allowed to react to form B according to the hypothetical gas-phase reaction A1g2¡B1g2. The following data are collected: Time (s) 0 40 80 120 160 Moles of A 0.100 0.067 0.045 0.030 0.020 (c) Which of the following would be needed to calculate the rate in units of concentration per time: (i) the pressure of the gas at each time, (ii) the volume of the reaction flask, (iii) the temperature, or (iv) the molecular weight of A?
The isomerization of methyl isonitrile (CH3NC) to acetonitrile (CH3CN) was studied in the gas phase at 215°C, and the following data were obtained:
Time (s) [CH3NC] (M)
0 0.0165
2000 0.0110
5000 0.00591
8000 0.00314
12,000 0.00137
15,000 0.00074
(a) Calculate the average rate of reaction, in M/s, for the time interval between each measurement. (c) Which is greater, the average rate between t = 2000 and t = 12,000 s, or between t = 8000 and t = 15,000 s?
The isomerization of methyl isonitrile (CH3NC) to acetonitrile (CH3CN) was studied in the gas phase at 215°C, and the following data were obtained:
Time (s) [CH3NC] (M)
0 0.0165
2000 0.0110
5000 0.00591
8000 0.00314
12,000 0.00137
15,000 0.00074
(d) Graph [CH3NC] versus time and determine the instantaneous rates in M/s at t = 5000 s and t = 8000 s.
The rate of disappearance of HCl was measured for the following reaction: CH3OH1aq2 + HCl1aq2¡CH3Cl1aq2 + H2O1l2 The following data were collected: Time (min) 3HCl 4 1M2 0.0 1.85 54.0 1.58 107.0 1.36 215.0 1.02 430.0 0.580 (a) Calculate the average rate of reaction, in M>s, for the time interval between each measurement.
The rate of disappearance of HCl was measured for the following reaction: CH3OH1aq2 + HCl1aq2¡CH3Cl1aq2 + H2O1l2 The following data were collected: Time (min) 3HCl 4 1M2 0.0 1.85 54.0 1.58 107.0 1.36 215.0 1.02 430.0 0.580 (b) Calculate the average rate of reaction for the entire time for the data from t = 0.0 min to t = 430.0 min.
