Consider the reaction A + B → C + D. Is each of the following statements true or false? (b) If the reaction is an elementary reaction, the rate law is second order.

Suppose that a certain biologically important reaction is quite slow at physiological temperature 137 _x001E_C2 in the absence of a catalyst. Assuming that the collision factor remains the same, by how much must an enzyme lower the activation energy of the reaction to achieve a 1 * 10^5-fold increase in the reaction rate?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Activation Energy
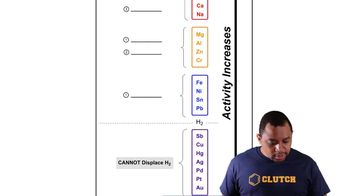
Enzymes as Catalysts
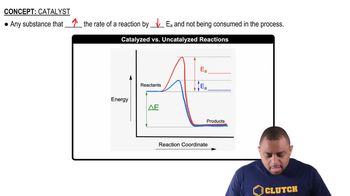
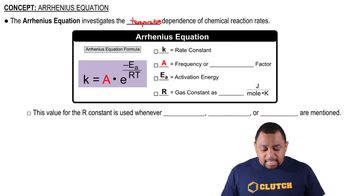
Arrhenius Equation
The enzyme urease catalyzes the reaction of urea, (NH2CONH2), with water to produce carbon dioxide and ammonia. In water, without the enzyme, the reaction proceeds with a first-order rate constant of 4.15 × 10-5 s-1 at 100°C. In the presence of the enzyme in water, the reaction proceeds with a rate constant of 3.4 × 104 s-1 at 21°C. (c) In actuality, what would you expect for the rate of the catalyzed reaction at 100°C as compared to that at 21°C?
The activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is 95 kJ/mol. The addition of a catalyst lowers the activation energy to 55 kJ/mol. Assuming that the collision factor remains the same, by what factor will the catalyst increase the rate of the reaction at (a) 25 C
The activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is 95 kJ/mol. The addition of a catalyst lowers the activation energy to 55 kJ/mol. Assuming that the collision factor remains the same, by what factor will the catalyst increase the rate of the reaction at (b) 125 °C?
Consider the reaction A + B → C + D. Is each of the following statements true or false? (c) If the reaction is an elementary reaction, the rate law of the reverse reaction is first order.
The reaction 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2 (g) is second order in NO and first order in O2. When [NO] = 0.040 M, and [O2] = 0.035 M, the observed rate of disappearance of NO is 9.3⨉10-5 M/s. (b) What is the value of the rate constant?
