The activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is 95 kJ/mol. The addition of a catalyst lowers the activation energy to 55 kJ/mol. Assuming that the collision factor remains the same, by what factor will the catalyst increase the rate of the reaction at (a) 25 C

Consider the reaction A + B → C + D. Is each of the following statements true or false? (b) If the reaction is an elementary reaction, the rate law is second order.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
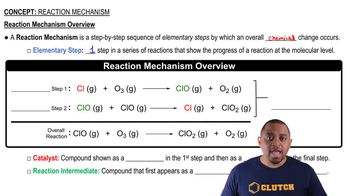
Elementary Reactions
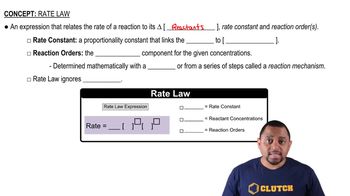
Rate Law
Order of Reaction

The activation energy of an uncatalyzed reaction is 95 kJ/mol. The addition of a catalyst lowers the activation energy to 55 kJ/mol. Assuming that the collision factor remains the same, by what factor will the catalyst increase the rate of the reaction at (b) 125 °C?
Consider the reaction A + B → C + D. Is each of the following statements true or false? (c) If the reaction is an elementary reaction, the rate law of the reverse reaction is first order.
The reaction 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2 (g) is second order in NO and first order in O2. When [NO] = 0.040 M, and [O2] = 0.035 M, the observed rate of disappearance of NO is 9.3⨉10-5 M/s. (b) What is the value of the rate constant?
The reaction 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2 (g) is second order in NO and first order in O2. When [NO] = 0.040 M, and [O2] = 0.035 M, the observed rate of disappearance of NO is 9.3⨉10-5 M/s. (c) What are the units of the rate constant?
