Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (c) Increasing the reaction temperature increases the fraction of successful collisions between reactants.
Ch.14 - Chemical Kinetics

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 14, Problem 58b
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (b) Exothermic reactions are faster than endothermic reactions.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
1. Understand the terms: An exothermic reaction is a chemical reaction that releases energy by light or heat. It is the opposite of an endothermic reaction, which absorbs energy in the form of heat.
2. Understand the statement: The statement is suggesting that exothermic reactions are always faster than endothermic reactions.
3. Analyze the statement: The speed of a reaction (reaction rate) is determined by factors such as temperature, concentration of reactants, presence of a catalyst, and surface area of reactants. It is not directly related to whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
4. Conclusion: Therefore, the statement 'Exothermic reactions are faster than endothermic reactions' is false. The energy change (exothermic or endothermic) does not determine the speed of the reaction.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are chemical processes that release energy, usually in the form of heat, to their surroundings. This release of energy often results in an increase in temperature of the surrounding environment. Common examples include combustion reactions, such as burning wood or fossil fuels.
Recommended video:
Guided course
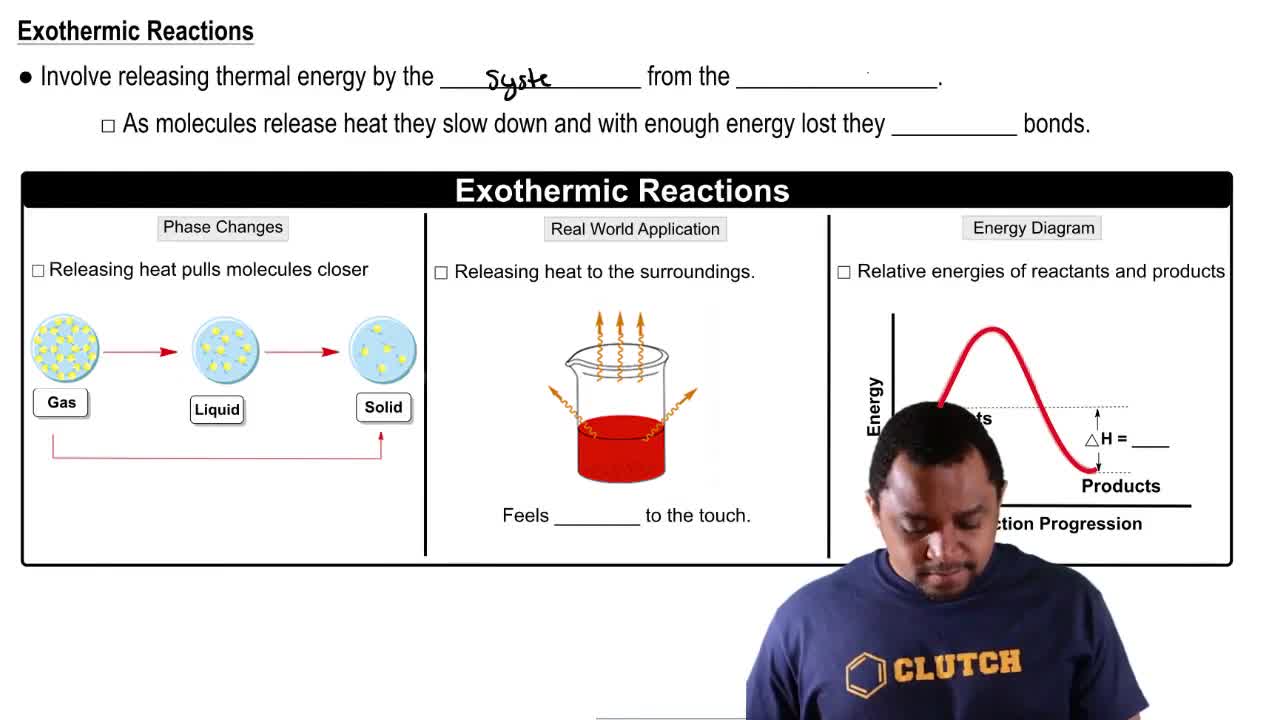
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Endothermic Reactions
Endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings, leading to a decrease in temperature of the environment. These reactions require an input of energy to proceed, which can come from heat, light, or electricity. Photosynthesis in plants is a classic example of an endothermic process.
Recommended video:
Guided course
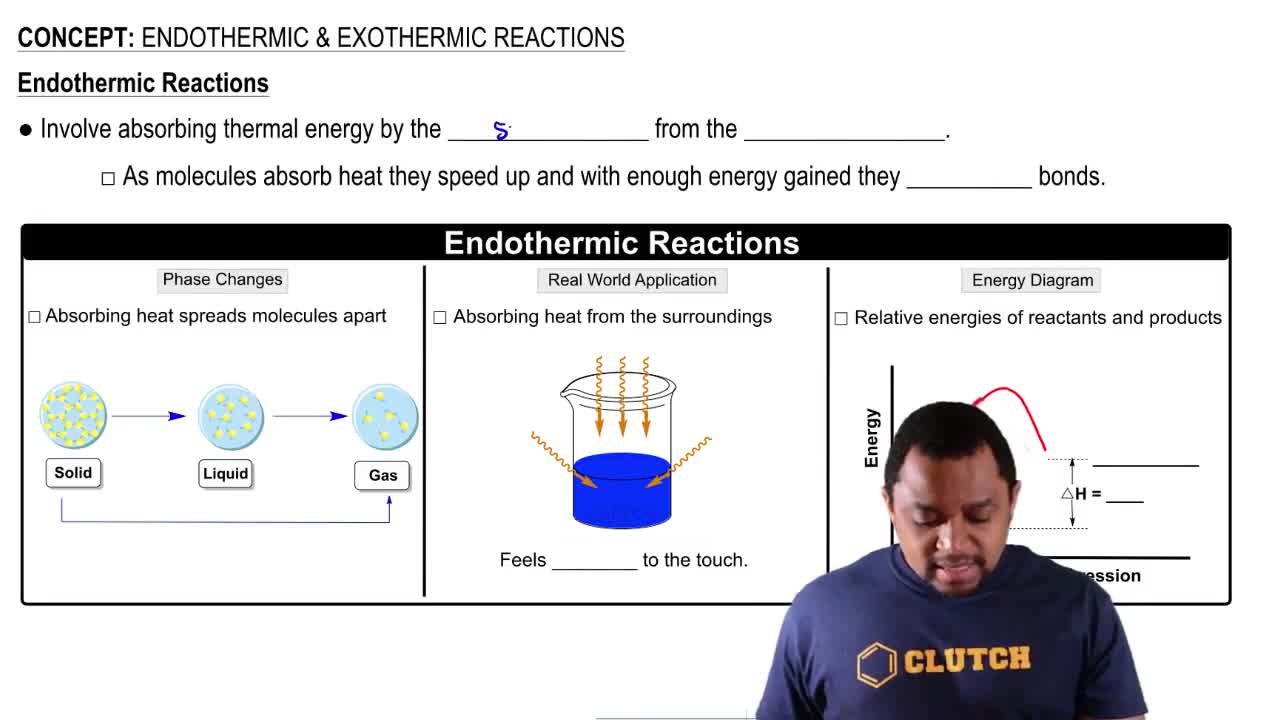
Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
Reaction Rates
The rate of a chemical reaction refers to how quickly reactants are converted into products. Factors influencing reaction rates include temperature, concentration, surface area, and the presence of catalysts. While exothermic reactions may release energy quickly, this does not inherently mean they are faster than endothermic reactions, as reaction rates depend on various conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
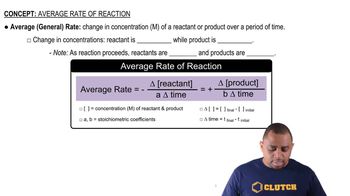
Average Rate of Reaction
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (a) If you measure the rate constant for a reaction at different temperatures, you can calculate the overall enthalpy change for the reaction.
2
views
Textbook Question
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (c) If you double the temperature for a reaction, you cut the activation energy in half.
1
views
Textbook Question
Based on their activation energies and energy changes and assuming that all collision factors are the same, rank the following reactions from slowest to fastest. (a) Ea = 45 kJ>mol; E = -25 kJ>mol (b) Ea = 35 kJ>mol; E = -10 kJ>mol (c) Ea = 55 kJ>mol; E = 10 kJ>mol
