The reaction between ethyl iodide and hydroxide ion in ethanol (C2H5OH) solution, C2H5I(alc) + OH-(alc) → C2H5OH(l) + I-(alc), has an activation energy of 86.8 kJ/mol and a frequency factor of 2.10 × 1011 M-1 s-1. (c) Which reagent in the reaction is limiting, assuming the reaction proceeds to completion?

Dinitrogen pentoxide (N2O5) decomposes in chloroform as a solvent to yield NO2 and O2. The decomposition is first order with a rate constant at 45 _x001E_C of 1.0 * 10^-5 s^-1. Calculate the partial pressure of O2 produced from 1.00 L of 0.600 M N2O5 solution at 45 _x001E_C over a period of 20.0 h if the gas is collected in a 10.0-L container. (Assume that the products do not dissolve in chloroform.)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
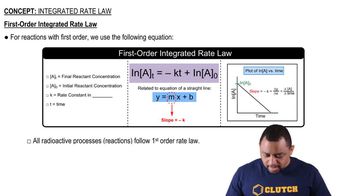
First-Order Reactions
Ideal Gas Law

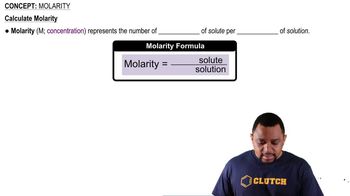
Concentration and Molarity
Enzymes are often described as following the two-step mechanism:
E + S ⇌ ES (fast)
ES → E + P (slow)
where E = enzyme, S = substrate, ES = enzyme9substrate complex, and P = product.
(a) If an enzyme follows this mechanism, what rate law is expected for the reaction?
Enzymes are often described as following the two-step mechanism:
E + S ⇌ ES (fast)
ES → E + P (slow)
where E = enzyme, S = substrate, ES = enzyme9substrate complex, and P = product.
(b) Molecules that can bind to the active site of an enzyme but are not converted into product are called enzyme inhibitors. Write an additional elementary step to add into the preceding mechanism to account for the reaction of E with I, an inhibitor.
The reaction between ethyl iodide and hydroxide ion in ethanol (C2H5OH) solution, C2H5I(alc) + OH-(alc) → C2H5OH(l) + I-(alc), has an activation energy of 86.8 kJ/mol and a frequency factor of 2.10 × 1011 M-1 s-1. (d) Assuming the frequency factor and activation energy do not change as a function of temperature, calculate the rate constant for the reaction at 50 C.
The gas-phase reaction of NO with F2 to form NOF and F has an activation energy of Ea = 6.3 kJ>mol. and a frequency factor of A = 6.0 * 108 M-1 s-1. The reaction is believed to be bimolecular: NO1g2 + F21g2 ¡ NOF1g2 + F1g2 (e) Suggest a reason for the low activation energy for the reaction.
